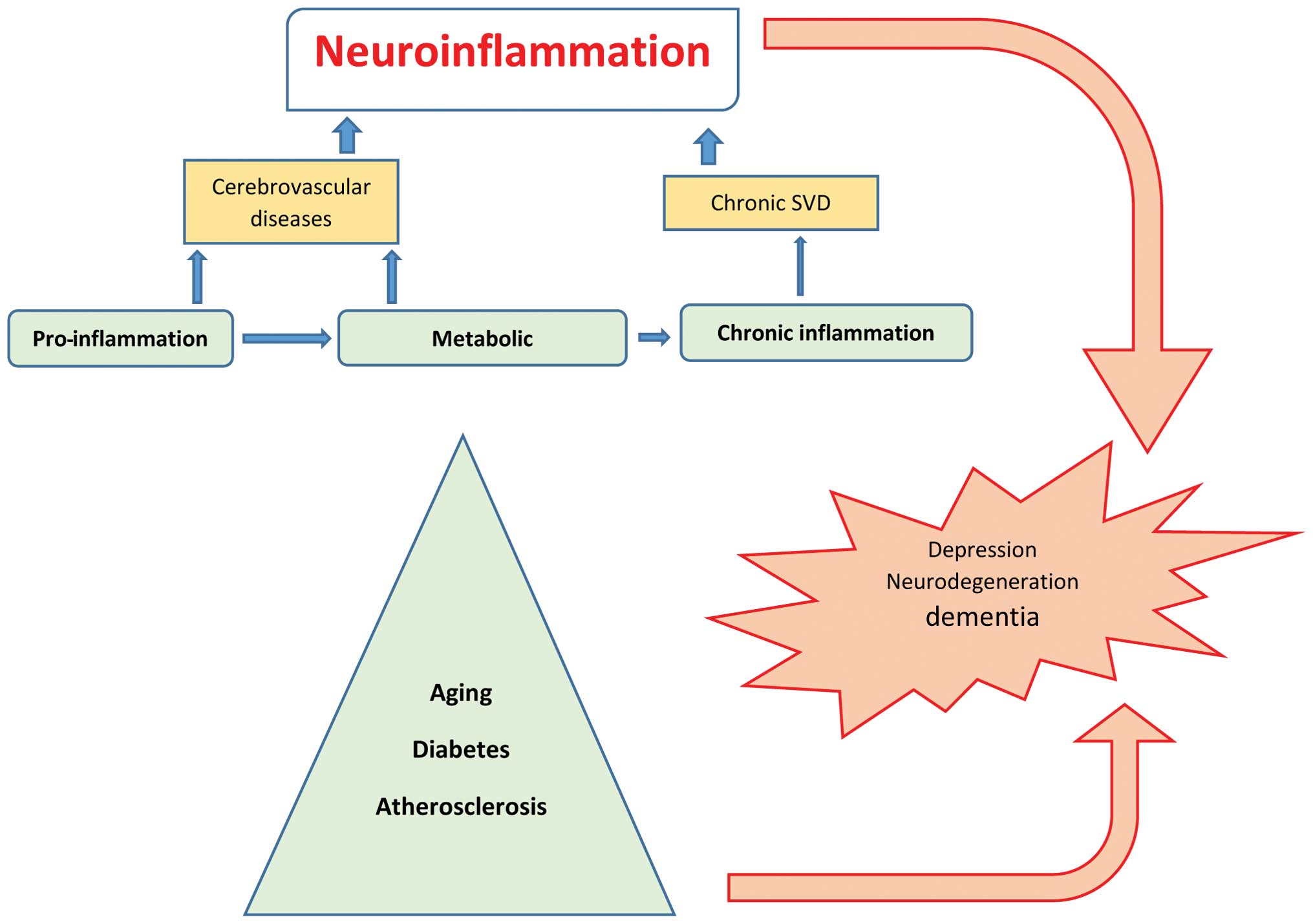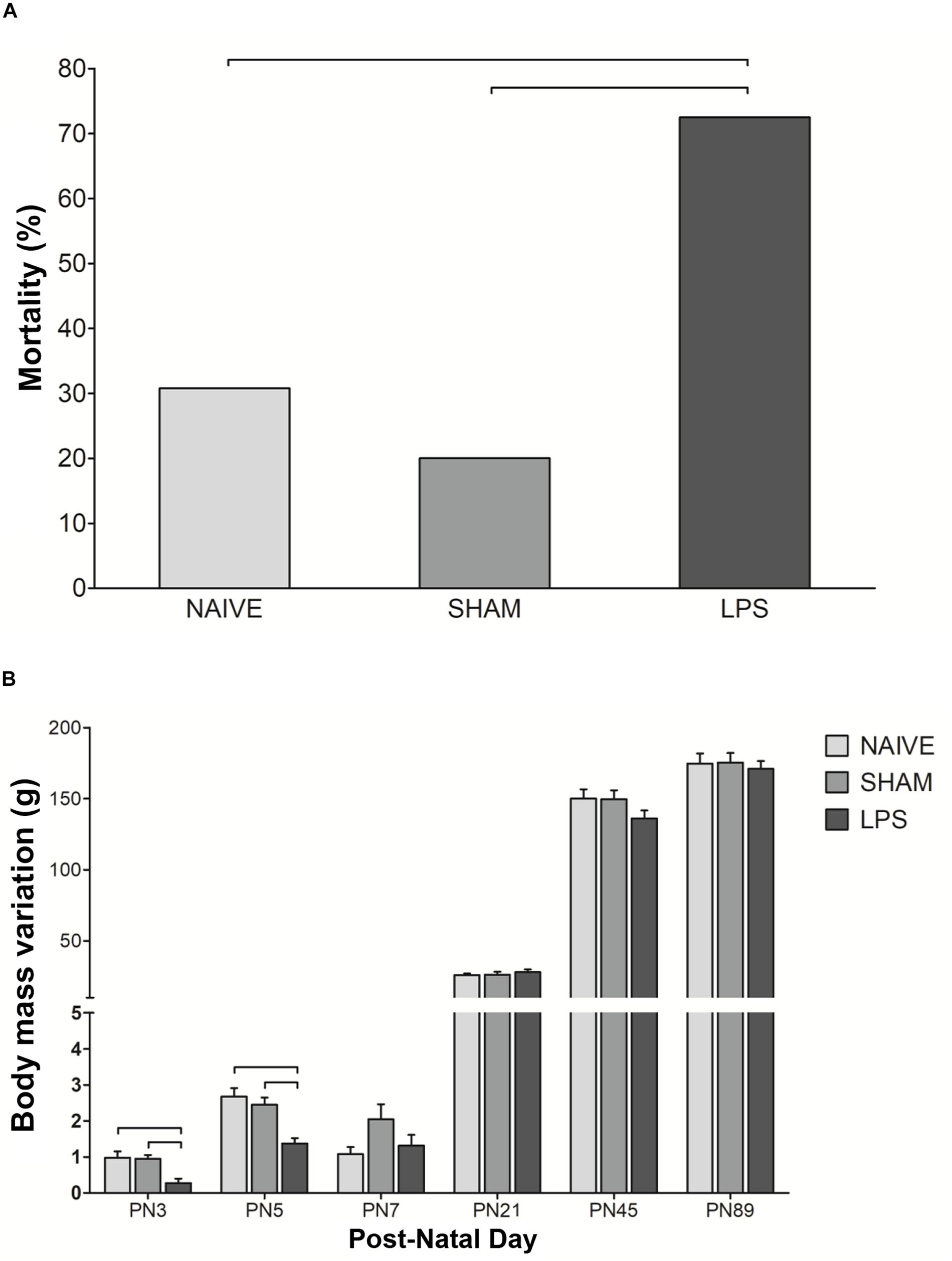
Frontiers | Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Systemic Inflammation in the Neonatal Period Increases Microglial Density and Oxidative Stress in the Cerebellum of Adult Rats | Cellular Neuroscience

HMGB1 Acts on Microglia Mac1 to Mediate Chronic Neuroinflammation That Drives Progressive Neurodegeneration | Journal of Neuroscience

Systemic LPS causes chronic neuroinflammation and progressive neurodegeneration - Qin - 2007 - Glia - Wiley Online Library

Systemic LPS causes chronic neuroinflammation and progressive neurodegeneration - Qin - 2007 - Glia - Wiley Online Library

Systemic LPS causes chronic neuroinflammation and progressive neurodegeneration - Qin - 2007 - Glia - Wiley Online Library

Chronic neuroinflammation generated by a single LPS injection (15 × 10⁶... | Download Scientific Diagram

Polydatin Prevents Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced Parkinson's Disease via Regulation of the AKT/GSK3β-Nrf2/NF-κB Signaling Axis | Semantic Scholar

DSP-4 induces chronic neuroinflammation with heterogeneous densities of... | Download Scientific Diagram
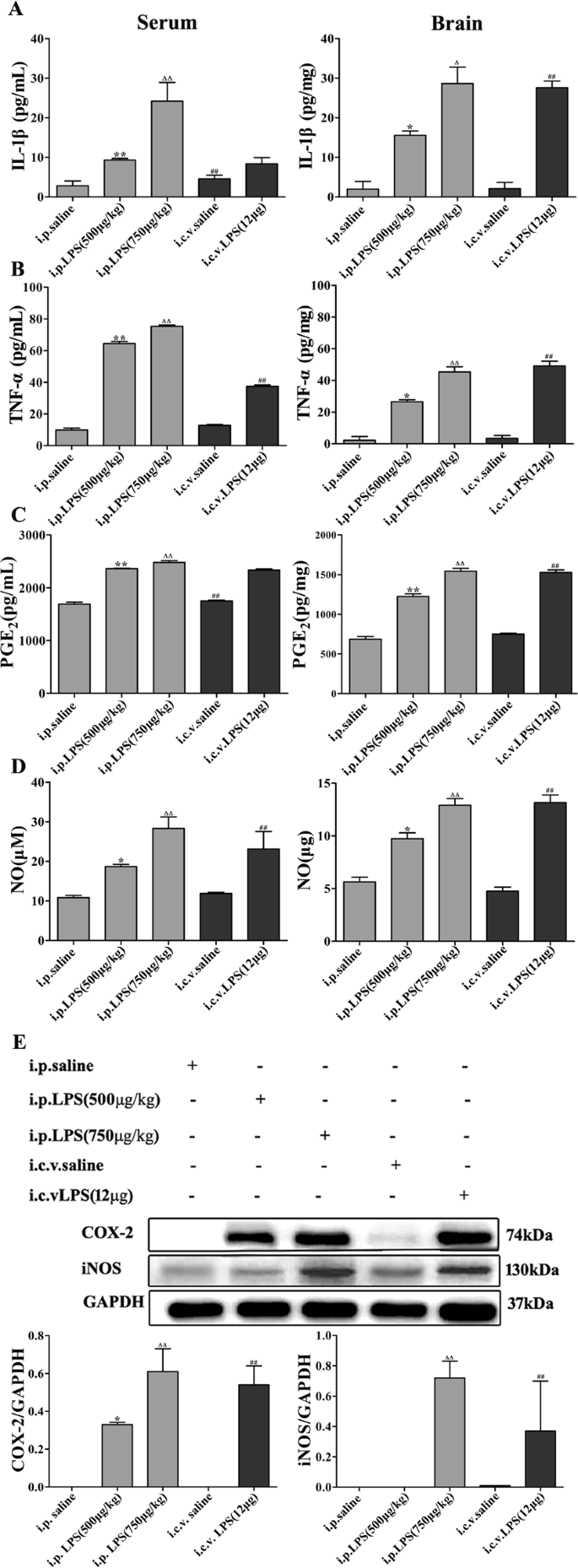
Neuroinflammation induced by lipopolysaccharide causes cognitive impairment in mice | Scientific Reports

Systemic LPS causes chronic neuroinflammation and progressive neurodegeneration - Qin - 2007 - Glia - Wiley Online Library

Osmotin attenuates LPS-induced neuroinflammation and memory impairments via the TLR4/NFκB signaling pathway | Scientific Reports

Systemic LPS causes chronic neuroinflammation and progressive neurodegeneration - Qin - 2007 - Glia - Wiley Online Library
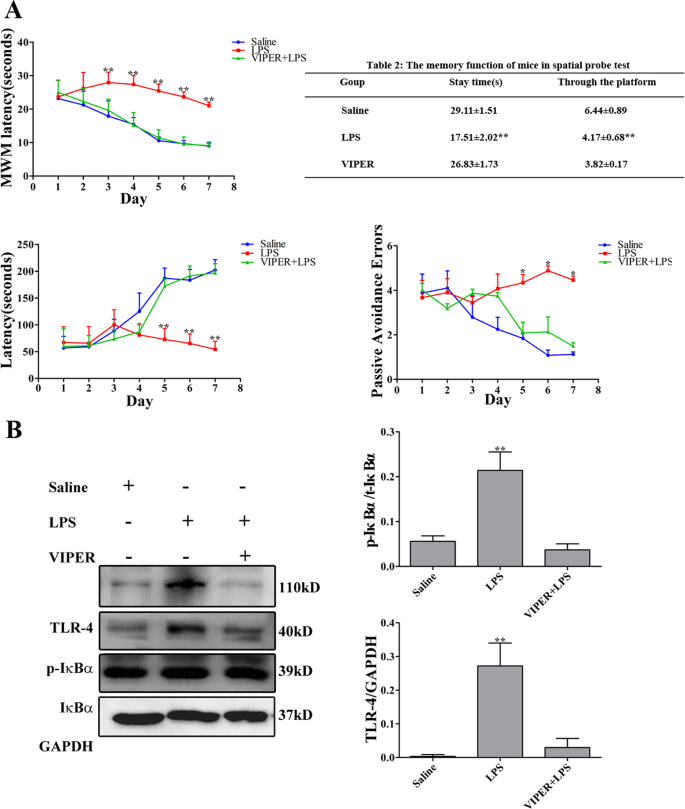
Neuroinflammation induced by lipopolysaccharide causes cognitive impairment in mice | Scientific Reports

Interplay among norepinephrine, NOX2, and neuroinflammation: key players in Parkinson's disease and prime targets for therapies

Systemic LPS causes chronic neuroinflammation and progressive neurodegeneration. - Abstract - Europe PMC
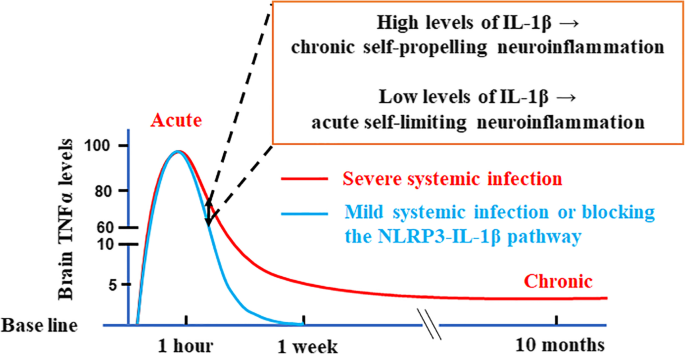
A novel role of NLRP3-generated IL-1β in the acute-chronic transition of peripheral lipopolysaccharide-elicited neuroinflammation: implications for sepsis-associated neurodegeneration | Journal of Neuroinflammation | Full Text
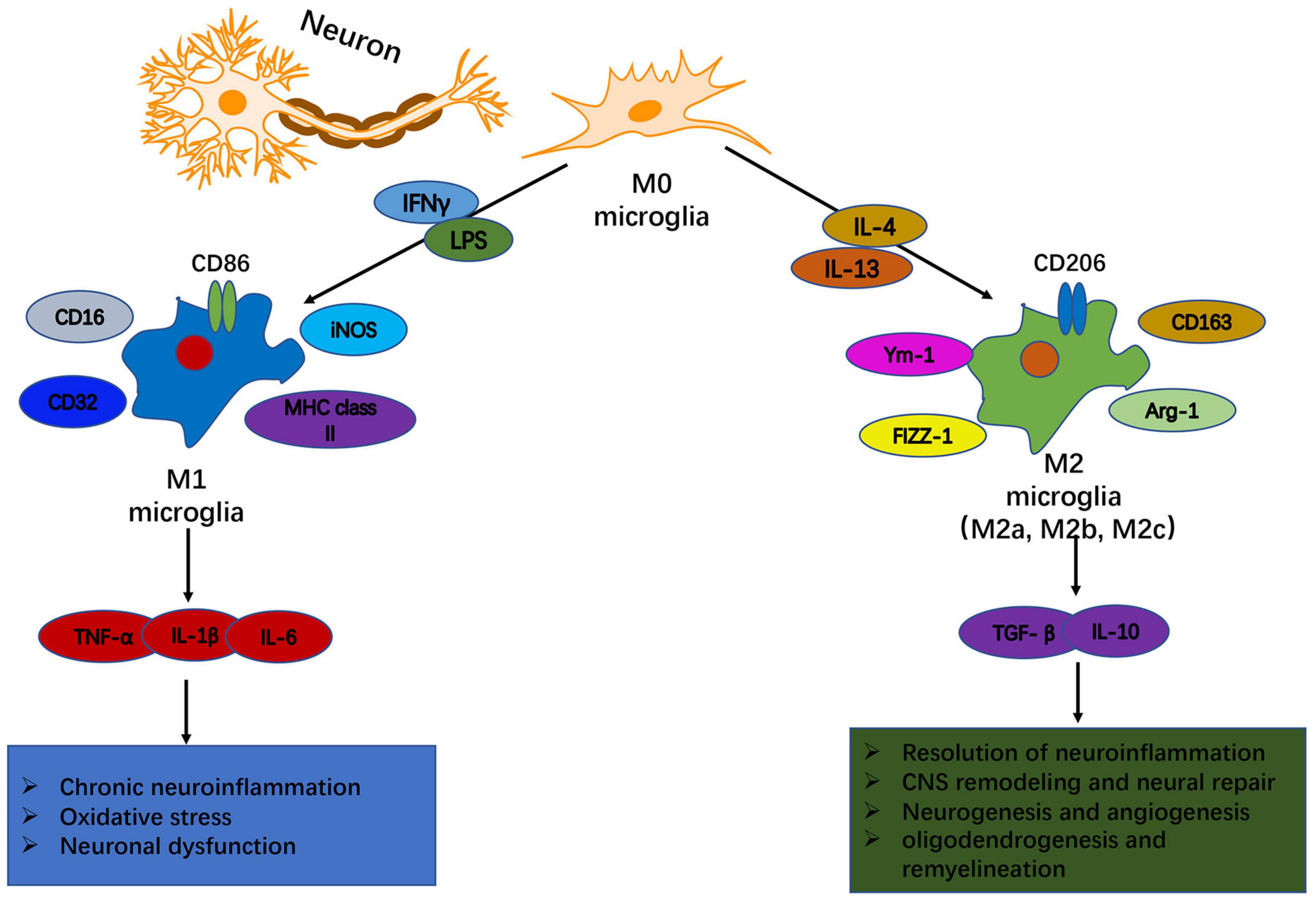
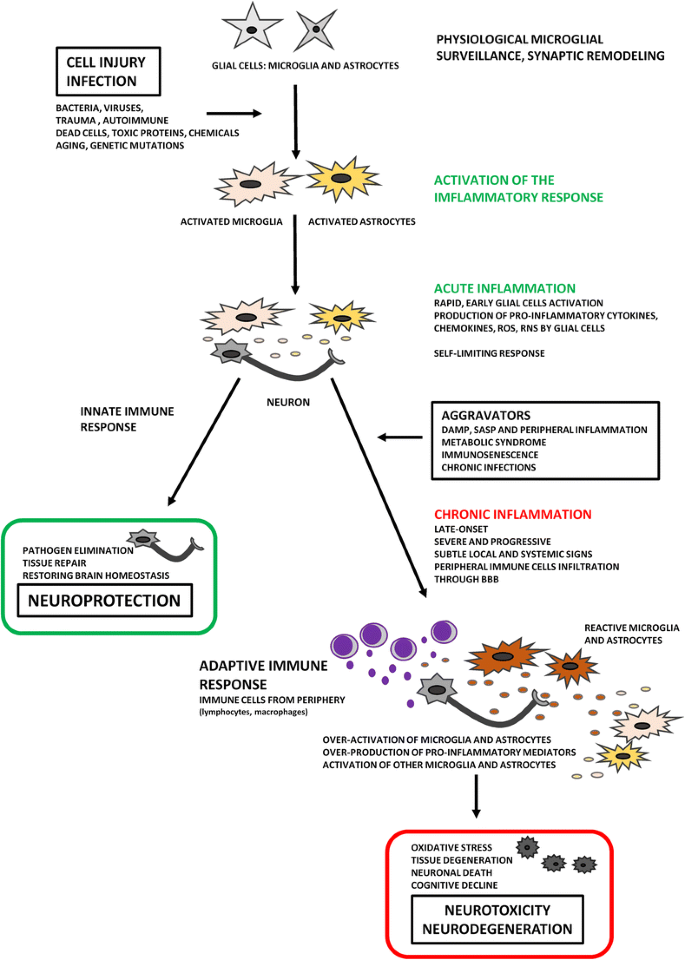
Frontiers | Microglia and Neuroinflammation: Crucial Pathological Mechanisms in Traumatic Brain Injury-Induced Neurodegeneration | Aging Neuroscience